Introduction
Did you know that over $4 billion is lost to financial fraud annually in the US alone? Inaccurate financial reporting can have devastating consequences, shaking investor confidence and crippling entire industries. This is where financial statement audits come in – acting as a vital safeguard for financial transparency and trust.
Why are Financial Statement Audits Important?
Financial statement audits serve multiple critical purposes:
- Building Trust and Credibility: Audited financial statements provide independent verification, assuring stakeholders like investors, credit rating agencies, and regulators that the information presented is reliable. This fosters trust in the financial markets and encourages investment.
- Ensuring Compliance: Audits ensure companies adhere to accounting standards and regulations, minimizing the risk of legal or financial penalties.
- Identifying Risks and Improving Controls: Auditors can pinpoint areas where financial reporting might be vulnerable to errors. They then recommend improvements to internal controls, the safeguards a company has in place to ensure accurate financial reporting.
- Detecting and Preventing Fraud: A thorough audit may uncover fraudulent activities, protecting a company's assets and reputation.
"Financial statement audits are foundational to the financial reporting ecosystem. They ensure that stakeholders can trust the accuracy and reliability of the financial information presented." - Gartner, Financial Reporting Insights
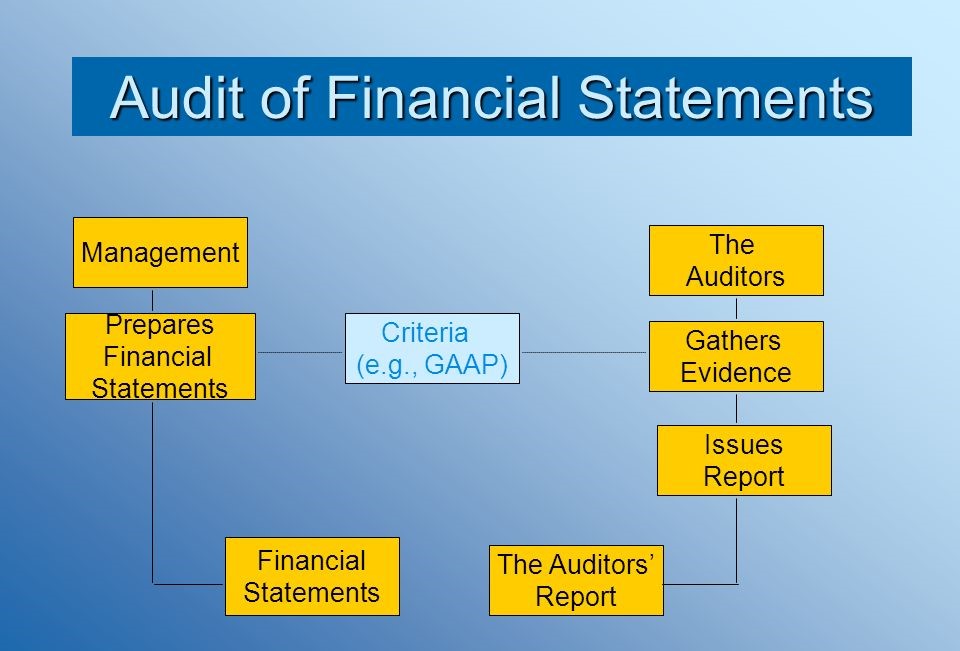
The Financial Statement Audit Process
1. Planning and Risk Assessment:
Auditors gain a deep understanding of the client's business and industry. They identify potential areas of risk, such as complex revenue recognition or high-value inventory, and tailor the audit plan accordingly.
2. Internal Control Evaluation:
Auditors assess the effectiveness of the client's internal controls for preventing and detecting errors or fraud. They test these controls to verify their reliability.
3. Substantive Procedures:
This stage involves in-depth testing of account balances and transactions. Auditors gather evidence to support the accuracy of the financial statements.
4. Audit Report Issuance:
The audit culminates in a formal report expressing the auditor's opinion on the fairness and accuracy of the financial statements. The report also communicates any findings and recommendations to management and the board.
Streamlining Financial Statement Audits with CollabAuditAI
Imagine a world where financial statement audits are revolutionized by CollabAuditAI, an advanced data and workflow management tool. Here's what CollabAuditAI can bring to the table:
- Faster and More Efficient Audits: CollabAuditAI eliminates the tedious task of manually collecting and integrating data from various sources. It automates this process, freeing up valuable auditor time for analysis and providing deeper insights.
- Enhanced Transparency and Collaboration: Real-time access to audit progress and findings through CollabAuditAI fosters better communication between the audit team and the company. This allows for prompt issue resolution and smoother collaboration throughout the audit process.
- Reduced Risk of Errors: Automated tasks and data validation checks within CollabAuditAI minimize the risk of human error, leading to more reliable and accurate audits.
- Data-Driven Recommendations: Powerful analytics capabilities in CollabAuditAI can uncover hidden patterns and trends in financial data. This empowers auditors to identify potential risks and provide more valuable recommendations for improving financial practices.
Conclusion
By leveraging CollabAuditAI, companies can experience a significant transformation in their financial statement audits. This innovative tool streamlines the process, improves transparency, and empowers auditors to deliver a more insightful and valuable service. The use of advanced data and workflow management tools like CollabAuditAI ensures that financial audits are more accurate, efficient, and insightful, ultimately supporting better financial decision-making and fostering trust in financial reporting.
